| As hair is concerned from the aesthetic point of view is the most sensitive thing for both males & females. Loss of hairs can lead to various personality disorders and in some cases leads to social dissociations too. As we move to the various amenities and procedures available for the hair rejuvenation we would like to tell you something about hair anatomy and the disorders associated with it in a brief.There are approximately 5 million hairs on our body. Of these, about 150,000 (more if you’re blond, less if you’re a redhead) are found on our scalp. We have got no hair follicles on the palms, soles, lips, tip of the penis, clitoris, and labia minora (small “lips” of the vagina).
Our skin contains a pocket called hair follicle which gives rise to the hair. During its growing phase, the follicle has a bulb-shaped bottom, the center of which is called the dermal papilla .The papilla is fed by very small blood vessels, which bring it food and oxygen and take wastes away. The papilla is highly sensitive to hormones. It is here that hormones and chemicals secreted by your body (or injested as a medicine) work on the hair, making it grow faster, slower, or not at all.
The hair color is determined by pigmented cells growing at the dermal papilla. These cells are melanocytes, contain a chemical pigment (melanin). The exact color of our hair is determined by the density and amount of this pigment. Two types of melanin are found, one coloring hair brown to black (eumelanin) and one coloring hair blond to red (pheomelanin). The color, shape and thickness are genetically determined.
Hair follicle is a sac-like structure, surrounds the hair root, found below the skin, and has very small blood vessels giving it nutrition. Sebaceous glands surrounding the hair root secrete oil (sebum) while salt-water (perspiration) is secreted from nearby sweat glands. The sebum oil protects the hair and keeps it shiny and waterproof, while the sweat is a way for the body to cool down if it’s too hot.
The function of hair is to keep the warmth in. The warm-blooded mammals need a warm body temperature to survive (cold-blooded animals, like snakes and other reptiles, metabolize and survive at “room-temperature” and thus neither need, nor have, hair). A tiny hair muscle attached to each hair follicle, called the arrector pili, contracts when in a cold environment (or when fearful). This causes the hair to be pulled downwards so it stands up straight (goose-bumps or gooseflesh), and warm air is actually trapped between each hair. This functions like a layer of clothing, keeping warmth in.
Hair contains a protein called keratin. The same protein is found in our nails and in our skin. A strand of hair has three layers. The outermost layer is called the cuticle. It is transparent and acts to protect the inner layers. The innermost layer is called the medulla, and is composed of large baggy cells that may have a hollow-like appearance. Between these two layers is the cortex. The bulk and strength of hair is from this compact area of cells.
Hair shaft is composed of three layers
Cuticle- outermost layer
Cortex- middle layer
Medulla- innermost layer
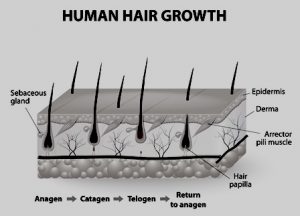
Human hair growth is cyclical i.e.
Anagen- Growing phase
Catagen- Involution phase
Telogen- Resting phase
Anagen, the active growth phase, lasts about 3-5yrs on the scalp. 80-90% of hairs on the scalp is in this phase only and grows at the rate of 0.37 mm/day. Catagen phase lasts for 2 weeks and telogen lasts about 3-5 months approximately.
Shorter anagen phase and longer telogen phase resulting in short hairs that stay in a place for long periods of time without growing longer, as most sites of our body having the same. |