HAIR AILMENTS & THE TREATMENTS AVAILABLE
Hair disorders:
Androgenetic Alopecia
Male –Pattern Baldness(MPB)
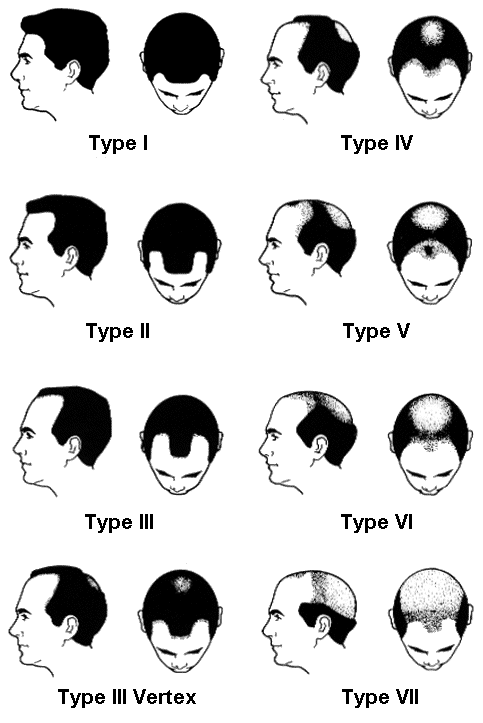
MPB shows itself during the teens 20’s or during early 30’s with gradual loss of hair, chiefly from the vertex and frontotemporal region. Presence of “whisker” or “kinky” hair may be the first sign of impending MPB. The anterior hair line recedes on each side , in Geheimratswinkeln(“professor angles”),so that the forehead becomes high. Several pattern of hair loss may exist but the most common is biparietal recession with loss on the vertex. The follicles produce finer and lighter hairs with each hair cycle until terminal hairs are replaced by vellus hairs.
Androgenic alopecia is likely caused by variety of genetic and environmental factors. Although researchers are studying the factors that may contribute to this condition, most of these remain unknown. Researchers have determined that this form of hair loss is related to the androgen receptor gene. The 5 alpha reduction of testosterone is increased yielding increased dihydrotestosterone(DHT).Androgen inducible TGF-Beta1derived from dermal papilla cells appears to mediate hair growth suppression. Male pattern baldness is caused by a genetic sensitivity of hair follicles to DHT, which causes them to shrink when exposed to it. This shortens their lifespan and prevents them from producing hair normally, Progressive shortening of anagen phase of hair growth is noted as the hair shaft diameter decreases, so the hairs are not only narrowing but are also shorter.
Histologically decrease in anagen and increase in telogen follicles is present.
Treatment-
Minoxidil- Topical application promotes the survivol of dermal papilla cells, prolongs anagen phase andresults in enlargement of shaft diameter. Available as 2,3,5 and 10%. Studies have showed 5% application in men is more affective in males. Those who respond must continue to use minoxidil indefinitely to maintain a response.
Finasteride- Type 2 5 alpha reductase inhibitor,is effective in preventing further hair loss and in increasing the hair count to the point of cosmetically appreciably results in men from 18-41 years. Effect seen after 6 months of use. If no result in 12 months discontinue its use.those who respond must use it indefinitely to maintain response.
Hair transplantation using micrografts of hair follicle from occipital to anterior scalp gives excellent cosmetic result.
Androgenetic(Pattern) alopecia in females:
Women generally have diffuse hair loss throughout the apical scalp with the part wider anteriorly. There is typical sparing of frontal hair line. The midline part is an important clinical clue, revealing a “Christmas tree pattern”of hair loss with the part tapering from the anterior to posterior scalp .
The same basic changes – reduced hair density and diameter, and diminished anagen and increased telogen hair occur in women too.
The cause is now believed to be a genetic predisposition with an excessive response to androgen.
Both women and men with pattern alopecia have higher levels of 5 alpha reductase and androgen receptor in frontal hair follicles compared to levels in occipital follicles.
Treatment- 2% minoxidil is the best choice for women.
Finasteride is of no use in women.
In some women ,telogen effluvium may cause worsening of pre-existing androgenetic alopecia.reversible causes of androgenetic alopecia like seborrheic dermatitis, thyroid disease , nutrient deficiency etc should be addressed.
Hair transplantation ,wigs or interwoven hair gives excellent cosmetic results.
Trichotillomania
Trichotillomania is the compulsive practice of pluckin hair from the scalp , brows or eye lashes. Typical areas are irregular patches of alopecia that contains hairs of varying length. Seen most commonly in girls below the age of 10 years. Usually a manifestation of an obsessive- compulsive disorder, but may also be associated with depression or anxiety. Trichophagia is compulsive swallowing of plucked hairs resulting in formation of gastric bezoar.
Histopathologically – empty anagen follicles, catagen hairs , pigment casts within the infundibulum, trichomalasia and hemorrhage will be demonstrated.
Treatment-Behaviour modification psychotherapy and appropriate psychopharmacological medication(such as serotonin reuptake inhibitor may be helpful.
Anagen Effluvium
Anagen effluvium usually results from a hair shaft fracture. Seen most commonly after administration of cancer chemotherapeutic agents, such as the antimetabolites , alkylating agents, and mitotic inhibitors. These agents result in temporary shutdown of hair matrix with resultant tapering of shaft (Pohl-Pinkus constrictions). Only anagen hairs are affected. The process is entirely reversible and hair follicle resumes its full activity in a few weeks.
Loose Anagen Syndrome
In this disorder the anagen hairs can be pulled from scalp with little effort. It occurs most commonly in blonde girls and is due to a defect in the hair cuticle.
Telogen Effluvium
Telogen effluvium presents with excessive shedding of normal telogen club hairs. It most commonly occurs 3 to 5 months after the premature conversion of many anagen hairs to telogen hairs induced by parturition, surgery, fever, drugs, dieting or traction. Application of Minoxidil may cause a brief telogen elluvium by premature termination of catagen necessary to initiate anagen. Shortening of anagen phase occurs in pattern alopecia and this causes telogen effluvium. Normally there is 10:1 ratio of anagen to telogen. This ratio decreases with progression of pattern alopecia.
Whatever the cause of hairloss, hair is always lost at the root. Telogen hair loss may be estimated by the hair pull test: grasping 40 hairs firmly between thumb and forefinger, followedby a slow pull that causes minimum discomfort to the patient. A count of more than 4-6 hairs is abnormal.
Treatment- No specific therapy is required for telogen effluvium. In the majority of patients hair loss with stop spontaneously and the hair will regrow. Prognosis is good is a specific event can be precipitated as the cause. Papulosquamous disorders , iron and thyroid disorders should be addressed and treated. Patient should be encouraged to eat a balanced diet.
Alopecia Areata
Alopecia areata(pelade in French) is characterized by rapid and complete loss of hair in one or more round or oval patches, usually on the scalp, bearded area eyebrows, eyelashes and less commonly on other hairy areas of the body. Patches are usually 1-5 cm in diameter. Early in the course there is sparing of grey hairs and white hairs are rarely affected.complete loss of scalp hair is referred to as alopecia totalis and complete loss of all hairs as alopecia universalis. Loss may occur confluent along the temporal and occipital scalp(ophiasis) or the entire scalpexcept this area(sisaipho).Clues too the correct diagnosis include a history of periodic regrowth,nail pitting and the presence of taperd fracture or exclamation point hairs. Etiology is probably auto-immune. Associated with other autoimmune diseases like SLE, thyroiditis, diabetes mellitus, myasthenia grevis and vitiligo.
Histology- In early disease there is lymphoid infiltrate in the peribulbar area of anagen or early catagen follicles.lmphocyte mediated damage to the bulb produces melanin incontinence in the surrounding stroma. Swarm of bees like appearance of infiltrate.follicles eventually miniaturise, appearing as small dystrophic anagen hairs high in the dermis, often with a persistent lymphocytic peribulbar infiltrate. The infiltrate distinguishes miniaturized follicle of alopecia areata from that of androgenetic alopecia
Treatment- Natural course of hair loss is very variable. Some hairs may regrow in few weeks without any treatment. Intralesional injection of corticosteroid is the treatment of choice. Triamcilonone 2-10 mg/ml, are typically given intradermally or in the superficial sub-cutaneous tissue. Pulsed oral corticosteroids in rapidly progressive or widespread disease have been reported in several studies.Attended risk of corticosteroid should be carefully weighed against the benefits as long term treatment is required to maintain regrowth.
Induction of contact sensitizer like squaric acid dibutyl ester,dinitrochlorobenzene, and diphencyprone may be useful in refractory cases.topical or oral methoxsalen and UVA light(PUVA therapy) are options for refractory or widespread lesions.Topical minoxidil have been tried alone or combined with other treatments. The 308-nm xenon chloride excimer laserhave been reported to provide regrowth in 11-1 2 sessions over a 9-11 week period. Can cause severe psychological stress and education about the disease and the disease process should be provided to the patient.
Predictors of poor prognosis are the presence of atopic dermatitis, childhood onset, widespread involvement, ophiais, duration of longer than 5 years, and onychodystrophy.
Newer modalities in the treatment of hair loss
PRP therapy (platelet rich plasma)
The hot buzz in treating hair loss is the new therapy known as PRP therapy.PRP stands for platelet rich plasma and has been used by hospitals and various surgical applications since 1970’s. In recent times it has been used in sports medicine and orthopedics to assist in speedy recovery.
Mode of action- when concentrated platelets of a person’s blood which contain protein and other particles are injected into the injury site, it helps to trigger the body’s ability to grow new soft tissue or bone cells to repair muscle. PRP involve application/injection of plasma that has about 5X the amount of platelets as in circulating blood. The platelets secrete numerous growth factors, including PDGF and VEGF, both of which have been shown to have positive effects on hair growth. So it is reasonable to think that PRP would not only help wound healing but also hair growth. Also reverts hair miniaturization caused by androgenetic alopecia or mald pattern baldness.
Preparation- Blood is taken from the patient and is centrifuged at high speed which will separate platelets from other component. Concentrated platelet rich plasma is then injected in the scalp.
A tiny scalp roller with spikes is used to stimulate the thinning area prior to injection. This sends the message to hair follicle to start the healing process. Then platelet rich plasma is injected to further stimulate stem cells in the follicle.
Useful in
- Androgenetic alopecia(males and females)
- Alopecia areata
- Telogen effluvium
- Graft survival after hair transplantation
- The procedure have to be repeated in about 6-8 months time
- Cost is 30000-40000 per treatment.
Stem Cell Therapy for hair loss:
Stem cells are specific cells in the body. In fact, we each started as a single stem cell, and divided into many cells and stem cells until we became a complete human body. As we age, these stem cells degenerate. If we get sick with illnesses such as cancer, heart disease, diabetes, neurodegenerative diseases, or auto immune diseases, our stem cells degenerate even more.
Through stem cell therapy, new stem cells are introduced to the body to repair or replace damaged cells. This is also called Regenerative Medicine, and for many, it can mean the difference between living and dying. Stem cell therapy can be given to patients through various means, including Embryonic Stem Cell Therapy (ESC), Fetal Stem Cell Therapy (FSC), Adult Stem Cell Therapy (ASC), Whole Cord Blood Stem Cell Therapy (CBSC), and Purified and Potentiated Cord Blood Stem Cell Therapy (PP-CBSC).
Again, Stem Cell Therapy can mean the difference between life and death for many people, but it can also help correct problems that are not fatal – such as hair loss. Scientists realized that if Stem Cell Therapy can help replace cells, it can be used to replace hair – particularly in cases of male pattern baldness. Many people have enjoyed great success with stem cell therapy while others do not see any results at all.
The stem cells are generated in a lab, and injected into the scalp. It typically takes more than one injection, on more than one occasion to see any results. This method of hair regeneration has been acclaimed globally.
One of the biggest concerns about stem cell therapy today is the fact that a patient’s body could essentially reject the stem cell replacements. This could prove to be instantly fatal for the patient. However, to date, there have been no reported incidents of any type of rejections when it comes to stem cell therapy for hair loss



 Dr Sachin k Maurya, Medical Director, Antiaging skin clinic Group
Dr Sachin k Maurya, Medical Director, Antiaging skin clinic Group